Andor Technology (Andor), an Oxford Instruments company and world leader…
ライフ・サイエンス
サービス
Maranaは、Andor最新の高性能sCMOSカメラプラットホームで、天文学や物理科学への利用に適しています。この度発売を開始した広視野Marana 4.2B-11背面照射sCMOSモデルは、量子効率 (QE) 95%、真空冷却による冷却温度は業界トップの -45 °Cを実現しました。
QE 95%、冷却温度 -45 °C: 超高感度背面照射sCMOSを導入
4.2 メガピクセル / 32mm センサ : 天文学に最適
NEW 高速モード: 動きの速い事象をスメアなく追跡
NEW 1.0 e- 低ノイズモード – 最も光が不足している状況向け
NEW 長時間露光機能 – より広い露光範囲で測光
Maranaは、Andor最新の高性能sCMOSカメラプラットホームで、天文学、ボースアインシュタイン凝縮、量子光学、ハイパースペクトルイメージング、中性子断層撮影、高速分光法などの物理科学分野の幅広い用途に適しています。この度発売を開始した広視野Marana 4.2B-11背面照射sCMOSモデルは、量子効率(QE)95%、真空冷却による冷却温度は業界トップの -45 °C を実現し、さらにピクセルサイズが光子捕捉に最適な11 µmです。 さらに32 mm対角という大型センサーの導入により、高いフレームレートと相俟って、このカメラを宇宙ごみの追跡や地球接近天体(NEO)の検出にも最適なものとしました。
sCMOS感度を究極化するというAndor独自の技術によって、微弱光状態においてもS/Nの最適化を可能とし、その結果、軌道を回る小型物体の追跡、微量濃度の分光検出、原子・イオンの離散量のBEC蛍光検出などに最適なものとなりました。感度が上がるということはすなわち露光時間を短くできるということであり、ダイナミックプロセスに対して48 fps という高フレームレートでの測定が可能となりました。Marana 4.2B-11 はQE曲線の選択が可能で、UVを強化した光源(BU)も選択肢に含めることにより、波長要件が260 nmと400 nmの間にある特定のアプリケーションにまでその用途が拡がります。 ダイナミックレンジを拡げる「デュアルオペレーショナルアンプリファイア」法は、太陽観測や分光材料特性化のように輝度の強弱が極端な領域が混在する難易度の高い場面の正確な可視化や定量化に最適な手法です。さらには、このクラス最高の定量精度を達成するために、Andorは搭載ソフトウェアの強化にも取り組みました。その結果、ダイナミックレンジ全域にわたり99.7%を超える市場をリードするリニアリティを実現しました。これは精密測光にとっても理想的なレベルといえます。
Marana 4.2B-11 は、2048 x 2048 ピクセル全域に有効なアクセスを可能にする独自のアンチグロー技術を活用して、画期的な 32mm 対角センサを導入し、高速フレームレートと組み合わせて天空スキャン天文観測に理想的なカメラを実用化しました。このカメラは高密度マルチファイバハイパースペクトルアプリケーションにも最適です。Maranaプラットホームは、波面補償光学センシングにも簡単に適用可能です。ROIを使用した数百fpsの画像取得が可能なだけでなく、データ転送ラグを最小化する特注設計にも対応可能です。


NEW Marana 4.2B-6:この高速モデルは74 fps(16ビット)を達成し、量子ガスダイナミクス、高速高解像度分光法、ハイパースペクトルイメージング、X線または中性子ラジオグラフィーによるサンプルダイナミクスの非破壊イメージングなど、高速フレームレートを必要とするイメージングまたは分光アプリケーションに使用できる最も感度の高い裏面照射型カメラです。多くのラボベースの光学イメージング構成やエシェル分光法での解像度マッチングに適しています。
Maranaプラットフォームは、補償光学の波面センシングに容易に適合させることができます。ROIで数百fpsを生成できるだけでなく、データ転送の遅延を最小限に抑えるように特別に設計されています。さらに、Maranaの高速フレームレートを利用して、画像やスペクトルの高速スタッキング(蓄積)により、ダイナミックレンジと効果的な井戸深度を大幅に拡張できます。
| Feature | Benefit |
| All Marana Models | |
| Up to 95% QE & lowest noise | Maximum signal to noise for light starved measurements. Detect smaller orbital debris; BEC fluorescence. |
| Vacuum cooled to -45°C | Very weak signals require lowest noise floor and longer exposures: Don’t be restricted by camera thermal noise! |
| 4.2 Megapixel | High pixel resolution, maintaining image clarity over an extended field of view |
| The ONLY vacuum back-illuminated sCMOS | Andor’s proprietary UltraVac™ technology protects the sensor from (a) QE degradation, and (b) moisture condensation |
| Extended Dynamic Range (EDR) Mode | ‘One snap quantification’ across the full dynamic range - perfect for Photometry. |
| > 99.7% linearity | Market leading quantitative accuracy over the whole signal range. |
| Fan and liquid cooling as standard | Liquid cooling for maximum sensitivity. |
| Adaptive Optics Ready | Minimize lag after data collection - transfer of row data immediately after exposing. |
| Spectroscopy Mode | On-board intelligence delivering spectroscopists-friendly spectra and multi-track data prior to transfer through CoaXPress or USB interface. Upfront data size reduction and easier user data processing. |
| 32-bit Binning Mode | Access huge dynamic range through extensive pixel binning. User-selectable data bit-depth up to 32-bit, transmitted upstream over the camera interface. |
| NEW Python Ready | Python wrapper integration and full supporting documentation in latest camera SDK helps integration and full control of custom-build systems. |
| USB 3.0 and CoaXPress connectivity options | USB 3.0 provides flexibility. CoaXPress enables the highest speeds to capture the most dynamic events |
| Marana 4.2B-11 (11 μm pixels) | |
| Glow Suppression Technology | Compensates the effects of sensor amplifier glow, allowing access to the full 4.2 Megapixel array. |
| 11 μm pixels and 32 mm sensor diagonal | Largest field of view sCMOS, compatible with wide range of acquisition times. Large sky scanning;Tomography. |
| Marana 4.2B-6 (6.5 μm pixels) | |
| 6.5 μm pixels | Smaller pixels better suited to some optical systems, e.g. echelle astrospectroscopy and cold atom imaging. |
| NEW Low Noise Mode | Reduces read noise down to 1.0 e- at the expense of pixel well depth. Ideal for light starved conditions, when absolute sensitivity is a priority. |
| NEW High Speed Mode | Acquire images at high speeds of up to 135 fps in full frame 16-bit mode via CoaXPress! Boost speeds even further using regions of interest. |
| NEW Global Clear Mode | Purges charge from all rows of the sensor simultaneously at the exposure start. Tight synchronization with pulsed sources. |
| NEW Long Exposure Capability | Enhanced Glow Suppression Technology enables exposures up to several minutes. |
| Model | Marana 4.2B-11 | Marana 4.2B-6 |
| Sensor Type | Back-Illuminated Scientific CMOS | |
| Array Size | 2048 (W) x 2048 (H) 4.2 Megapixel | 2048 (W) x 2046 (H) 4.2 Megapixel |
| Pixel Size | 11 x 11 μm | 6.5 x 6.5 μm |
| Image Area | 22.5 mm x 22.5 mm (31.9 mm diagonal) | 13.3 mm x 13.3 mm (18.8 mm diagonal) |
| Readout Modes | Rolling Shutter | Rolling Shutter and Global Clear |
| Pixel readout rate | 100 MHz (High Dynamic Range mode, 16-bit) 200 MHz (Fast Speed mode, 12-bit) |
310 MHz (Fast High Dynamic Range mode, 16-bit) 180 MHz (Low Noise mode, 12-bit) |
| Quantum Efficiency | up to 95% | |
| Read Noise (e-) median | 1.6 e- (at any readout rate) | 1.0 e- (Low Noise, 12-bit) 1.6 e- (High Dynamic Range, 16-bit) 1.9 e- (High Speed, 11-bit) |
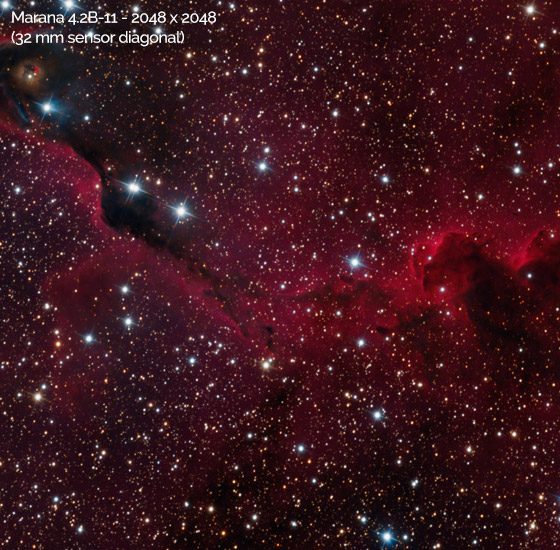
| Dark Current Air cooled (@-25°C ) Water/liquid cooled (@ -45°C) |
0.7 e-/pixel/s 0.3 e-/pixel/s |
0.15 e-/pixel/s 0.10 e-/pixel/s |
| Linearity | > 99.7% | |
| Photon Response Non-Uniformity (PRNU) | < 0.5% (@ half-light range) | |
| Data range | 16-bit (High Dynamic Range mode) 12-bit (Fast Speed mode) |
16-bit (Fast High Dynamic Range mode) 12-bit (Low Noise mode) |
| Interface | USB 3.0 - (CoaXPress available on request) | USB 3.0 and CoaXPress |
The Most Sensitive Back-illuminated sCMOS Available
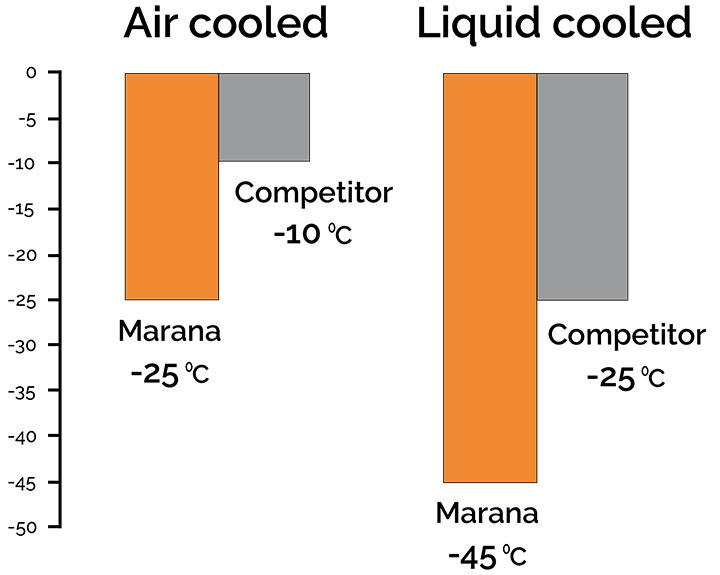
Marana back-illuminated sCMOS cameras feature 95% Quantum Efficiency (QE) and market-leading vacuum cooling down to -45 °C, minimizing noise floor. The darkcurrent of the GS400BSI and GS2020BSI sensors are significant contributors to overall system noise, so effective cooling becomes essential. With air cooling, Marana has almost 5x lower darkcurrent than the nearest physical science competing camera. Furthermore, the new low noise mode of Marana 4.2B-6 offers only 1.0 e- noise floor, ideal for the most light-starved use cases.
Having the most sensitive Back-illuminated sCMOS camera carries a host of practical advantages within Astronomy and Physical Sciences, for example:
Glow Suppression: Accessing the Entire Sensor Array with Longer Exposures

The GSense back-illuminated sensors from GPixel, present in the Marana models and some competing cameras, are widely recognised to suffer from glow at the edges of the sensor. Glow is especially prevalent in the GS400BSI sensor (used in Marana 4.2B-11), but is also present to a lesser extent in the GS2020BSI sensor (used in Marana 4.2B-6). This glow manifests as false signal and is exposure dependent. The competitor approach is either to (a) live with the glow; (b) only use the middle region of the sensor; or (c) firmware restrict exposure times to 30 milliseconds in order to contain the impact of glow on experiments! Either way, this fundamentally restricts performance and usefulness across a range of applications, either through field of view limitation or through sensitivity limitation.
Andor have studied and characterised this sensor issue in detail and have developed and implemented an ‘glow-suppression’ technology to suppress the effect of sensor glow on the image. This approach involves (a) shutting down glowing amplifiers during a large portion of the exposure and (b) mapping the impact of any residual glow across a wide exposure range and flat field correcting for it (on camera).
The figure to the right shows a dark image of the GSense400BSI back-illuminated sensor with and without glow suppression – the difference it makes is stark and has enabled Andor to open up the full 2048 x 2048 array, while also allowing users to access exposure times up to several seconds.
This Glow Suppression approach is very effective in widening the exposure range for the Marana models. The acceptable long exposure threshold will ultimately be defined by application usage. At longer exposures there will still be an elevated noise impact from the amplifier glow, especially at the sensor edges, so applications which require high SNR from the edge pixels may be limited to shorter exposure times. The table below is more of a guide, and ultimately, we advise that the practically usable exposure range should be tested by the end user.
| Minimum Exposure | Recommended Maximum Exposure | Hard coded Maximum Exposure (software) | |
| Marana 4.2B-6 | Microseconds | 5 minutes | 10 minutes |
| Marana 4.2-11 | Microseconds | 60 seconds | 10 minutes |
Guide only: Recommended Maximum Exposure for Marana models. We recommend that users test maximum usable exposure within the context of intended application usage.
Extended Dynamic Range and Superb Linearity
The innovative Dual Amplifier architecture of sCMOS sensors uniquely circumvents the need to choose between high or low gain amplifiers, in that signal can be sampled simultaneously by both high gain (low noise) and low gain (high capacity) amplifiers. As such, the lowest noise of the sensor can be harnessed alongside the maximum well depth, affording widest possible dynamic range. Uniquely for such a relatively small pixel design, this allows for dynamic range performance of 53,000:1 in Marana 4.2B-11.
Furthermore, on-camera intelligence delivers a significant linearity advantage, providing unparalleled quantitative measurement accuracy across the full dynamic range.
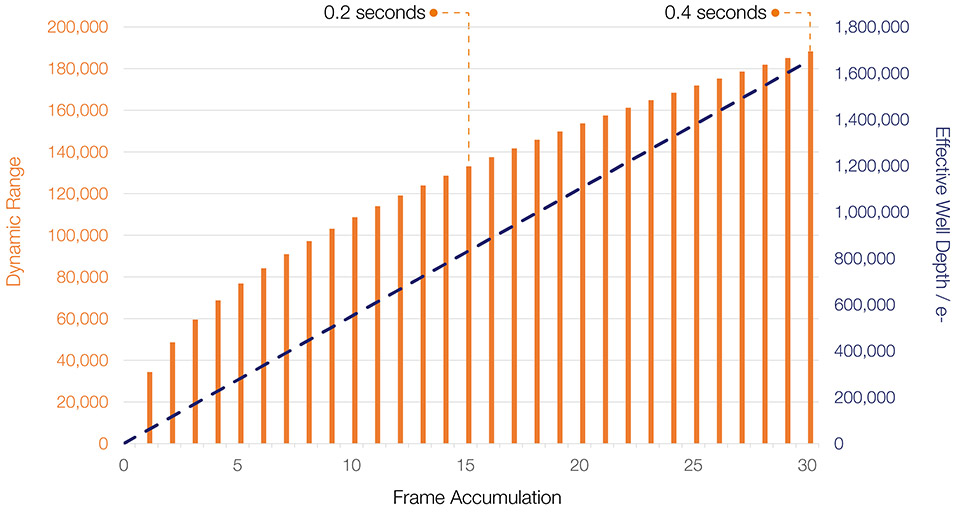
The fast, low noise readout of Marana sCMOS is also ideal for massively extending dynamic range through rapid stacking (accumulation) of multiple frames. For example, the plot below shows Dynamic Range and Effective Well Depth as a function of the number of stacked (accumulated) frames, plotted for Marana 4.2B-6. A Dynamic Range of 188,280:1, and a corresponding Effective Well Depth of 1,650,000 electrons can be reached with only 30 stacked frames. At maximum frame rate, this number of accumulated frames takes only 0.4 secs to acquire, achieving > 2 fps. This capability is significant for a range of challenges across imaging and spectroscopic characterisations.
Fast Frame Rates
The sCMOS sensors in Marana 4.2B-6 and Marana 4.2B-11 have highly parallel readout architecture, facilitating high data readout rates and therefore fast frame rates. All columns possess their own Amplifier and Analogue to Digital Converter (ADC), meaning that all columns are read out in parallel. Region of Interest (ROI) can be utilized to considerably boost frame rates further.
Marana 4.2-6 offers particularly fast frame rate capability of 74 fps (full array) with 16-bit data range, or a new High-Speed Mode of 135 fps with 11-bit data range. This renders it ideal for dynamic applications while avoiding motion smear, such as Quantum Gas (e.g. BEC) dynamics or Hyperspectral Imaging.
Marana 4.2-11 combines rapid frame rates with extended field of view, ideal for applications in astronomy such as Space Debris and NEO tracking, Pulsar imaging, Solar polarimetry and Lucky imaging/Speckle Interferometry.
Marana models are architected to offer both 16-bit and 12/11-bit modes. Lower bit depth modes are selected specifically to accelerate frame rates, while sacrificing wide dynamic range, useful for imaging fast phenomena that are exclusively low light, such as following dynamics on discrete numbers of fluorescent ultra cold atoms/ions.
| ROI Size (W x H)) | Max Frame Rate (fps) USB 3.0 (CXP) | |
| 16-bit Mono16 | 11-bit (High Speed) Mono12 Packed | |
| 2048 x 2048 | 43 (74) | 48 |
| 1400 x 1400 | 92 (108) | 120 (198) |
| 1200 x 1200 | 125 (126) | 164 (230) |
| 1024 x 1024 | 147 (147) | 231 (270) |
| 512 x 512 | 294 (294) | 536 (539) |
| 256 x 256 | 582 (582) | 1061 (1061) |
| 128 x 128 | 1148 (1148) | 2073 (2073) |
Rolling Shutter and Simulated Global Shutter
Both Marana models utilize a Rolling Shutter exposure mechanism. Rolling shutter essentially means that different lines of the array are exposed at different times as the read out ‘wave’ sweeps through the sensor, a row at the bottom starting the exposure approximately 21 ms before rows at the sensor’s distal edge. The lowest readout noise and fastest frame rates are available from this mode. Rolling shutter only presents an issue when imaging relatively large, fast-moving objects within the field. Then, aside from the risk of motion blur that can affect any imaging condition in which rate of motion is being temporally under-sampled, there is an additional possibility of rolling shutter spatial distortion. However, distortion is less likely when relatively small objects are moving at a rate that is being temporally oversampled by the frame rate, which in fact describes the vast majority of use cases.
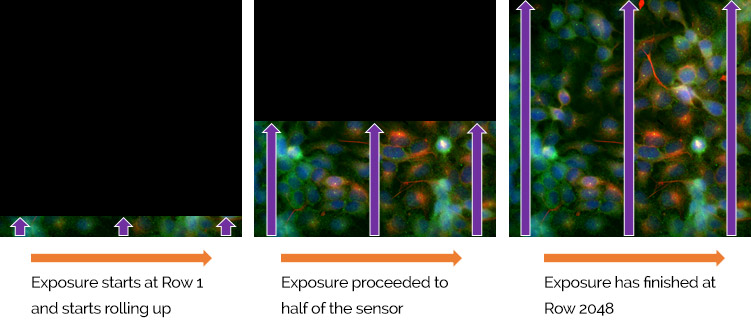
A further potential downside of rolling shutter is that different regions of the exposed image will not be precisely correlated in time to other regions, which can be essential for some applications. For example, if a cell is electrically stimulated and it is important to measure the onset of calcium sparks relative to the stimulation event, then rolling shutter should not be used. In this case, a true global shutter mode is required, available in ZL41 Wave 5.5 sCMOS cameras.
Multiple Optical Mount Options
Marana 4.2B-11 ships as default with standard F-mount optical coupling, however, the user can readily convert the camera for use with a C-mount lenses, simply by selecting this additional optical mount accessory at time of order. C-mount may be used with cropped sub-array sizes up to 1400 x 1400, yielding a 22mm sensor diagonal.
For attachment to various professional telescope configurations, the Marana 4.2B-11 front end can be direct mounted, providing f/# 0.7 with 72° cone angle. Through engagement with Andor’s Customer Special Request (CSR) service, custom mount faceplates can be tailored to your specific optical needs.
Likewise, while the smaller field of view Marana 4.2B-6 ships as native C-mount, an F-mount accessory may be ordered to convert the camera for use with F-mount lenses, for example to access lower f# input.
Fast Spectroscopy Mode
Marana 4.2B-6 and Marana 4.2B-11 can be readily adapted to the needs of fast spectroscopy, yielding up to greater than 11K spectra/sec. Such spectral rates are ideal for following fast reaction dynamics on sub-millisecond stopped flow timescales. Fast spectral kinetics capability can also be used for ‘pseudo-gated’ time-resolved functionality, whereby the first series of spectra from a fast series can be discarded to ‘gate out’ the effects of the initial exciting laser pulse.
On-camera FPGA real time asymmetric pixel binning allows for optimized optical matching and maximum photon collection, while a complimentary on-camera bit depth of 32-bit capability allows for very high binned effective well depths, ideal for fast transient absorption measurements.
Spurious Noise Filter
Andor’s Marana sCMOS camera comes equipped with an in-built FPGA filter that operates in real time to reduce the frequency of occurrence of high noise pixels. This real time filter corrects for pixels that would otherwise appear as spurious ‘salt and pepper’ noise spikes in the image.
The appearance of such noisy pixels is analogous to the situation of Clock Induced Charge (CIC) noise spikes in EMCCD cameras, in that it is due to the fact that we have significantly reduced the noise in the bulk of the sensor that the remaining small percentage of spuriously high noise pixels can become an aesthetic issue. The filter employed dynamically identifies such high noise pixels and replaces them with the mean value of the neighbouring pixels.
FPGA Timestamp
The Marana platform can generate a timestamp for each image that is accurate to 25 nanoseconds. Accurate timestamps can be important where precise knowledge of frame time impacts temporal dynamic analysis. This is especially important for fast events, where computer and interface latencies need to be considered, for example in Pulsar studies.
Flexible pixel binning
The Marana models feature on-camera flexible pixel binning, user definable to 1 pixel granularity. Greater binning flexibility can be useful for some photon starved applications where resolution can be sacrificed in favour of enhanced photon collection area per pixel - e.g. extremely low light luminescence experiments.
GPU Express
The Andor GPU Express library has been created to simplify and optimize data transfers from camera to a CUDA-enabled NVidia Graphical Processing Unit (GPU) card to facilitate accelerated GPU processing as part of the acquisition pipeline. GPU Express integrates easily with SDK3 for Andor sCMOS cameras, providing a user-friendly but powerful solution for management of high bandwidth data flow challenges; ideal for data intensive applications such as Light Sheet Microscopy, Super-Resolution Microscopy and Adaptive Optics.